1
Oct
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on The Experts Conference Europe 2012
A few weeks ago my neighbors were likely wondering why I constantly was playing the song Barcelona from Queen (Freddie Mercury & Montserrat Caballé). I had received the invitation to TEC Europe 2012 in Barcelona.
This will be the first time that I deliver sessions about Exchange Server 2013.
The session titles are “Built-In Functions in Exchange Server 2013 to Control and Monitor Important Mailboxes” and “Preventing Information Leakage with Information Rights Management”.
The first session covers compliance functions in Exchange Server 2013. The second session explains how to use AD RMS in Windows Server 2012 with Exchange Server 2013 and Windows Azure AD Rights Management in Office 365 Wave 15.

1
Oct
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Microsoft Exchange Connections Fall 2012
A few weeks ago I received an invitation to deliver sessions at Microsoft Exchange Connections in Las Vegas. I was very happy about this opportunity. Exchange Connections 2005 in San Diego was my first conference in the US, and I have good memories to things like the interview with Kevin that was recorded during a previous conference. These events were one of the biggest advantages while working with HP.
I am really looking forward to come back to this event. I will deliver a session about RBAC, a session about RMS and one about compliance features to control and monitor important mailboxes.

16
Apr
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Controlling Automatic Message Forwarding Using the Remote Domain Configuration
There are multiple options available how you can configure that emails received by a mailbox are automatically forwarded to another recipient.
A user can create an inbox rule to forward mails to another recipient. In Office 365 a user can use the Connected Accounts Tab in the Exchange Control Panel (ECP) to configure Forwarding of all mails delivered to his Exchange Online mailbox. The SMTP address specified in the Connected Accounts tab is written to the Active Directory attribute msExchGenericForwardingAddress. In the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) this attribute is called ForwardingSmtpAddress.
An Exchange administrator can use the Exchange Management Console (EMC) and define the mail forwarding settings of a mailbox in the Mail Flow Settings / Delivery Options tab. The administrator has to pick an existing object from the Global Address List (GAL) as forwarding target. Usually the Exchange administrator will create upfront a mail contact for this purpose. The Active Directory (AD) attribute altRecipient stores the distinguished name of the referenced object in the GAL. In the EMS this is visible as ForwardingAddress.
You can configure that a copy of the mail is stored in the local mailbox before the mail is forwarded to the final recipient. In EMS the parameter is called DeliverToMailboxAndForward and the related AD attribute is deliverAndRedirect.
It can be a security issue for a company if users are able to automatically forward their mails to an external mailbox. Therefore, very often Exchange administrators have to restrict this feature to enforce the security policy of the company.
An Exchange administrator can use the Remote Domain configuration to control message forwarding. You can use the AutoForwardEnabled parameter of the Set-RemoteDomain cmdlet to control this feature.
In customer projects I have frequently the requirement that end users should not be able to automatically forward emails. Only in exceptional cases an Exchange administrator should configure forwarding for a specific mailbox.
|
Forwarding Method
|
AutoForwardEnabled = True
|
AutoForwardEnabled = False
|
|
Inbox Rule
|
Message delivered
|
Message blocked
|
|
ForwardingSmtpAddress
|
Message delivered
|
Message blocked
|
|
ForwardingAddress
|
Message delivered
|
Message delivered
|
Based on the information provided in the previous table, it looks like an administrator can effectively achieve this requirement by setting AutoForwardEnabled = False and configure a ForwardingAddress for the specific mailbox using EMC or EMS.
End users are not able to modify the ForwardingAddress using an ECP menu option and they do not have access to the EMC.
However, end users are able to modify the ForwardingAddress using Remote PowerShell!
The default management role assignment policy assigned to a mailbox includes the Set-Mailbox cmdlet with the ForwardingSmtpAddress and the ForwardingAddress parameter. Luckily users have to specify an existing recipient object in the GAL with the ForwardingAddress parameter. It is unlikely that a mail contact exists in the GAL for their private mailbox. An option to prevent users from bypassing the remote domain configuration is to modify the management role assignment policy of regular mailboxes. You can remove the ForwardingAddress parameter from the Set-Mailbox cmdlet assigned to their mailbox.
30
Jan
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Changes not Visible in the Exchange Audit Log
I am currently working in a project where the customer will move their mailboxes to a private cloud operated by a service provider. The customer is concerned that the service provider staff might read his mails.
In Exchange Server 2010 you can use Mailbox Audit Logging to log access to a mailbox. You have to enable mailbox audit logging upfront per mailbox if you want to know who accessed a specific mailbox. You can use Administrator Audit Logging to log the commands that an Exchange administrator executed via the Exchange Management Shell, Exchange Management Console, or the Exchange Control Panel. If an administrator assigns someone full access rights to a mailbox, then the Administrator Audit Log would contain the corresponding command entry.
However, it is very important to realize that Administrator Audit Logging does not audit changes made via non Exchange management tools, for example, Active Directory management tools.
I would like to provide a simple example. Let’s assume you have a mailbox called “Big Boss” and there is a malicious administrator called “BadAdmin”.
Initially the Active Directory attributes of the user account Big Boss looks like this.
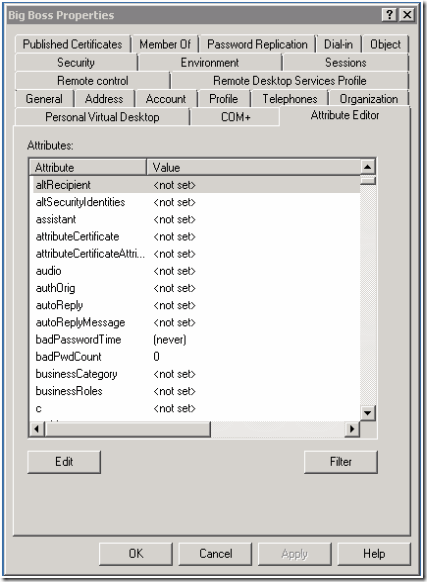
Figure 1: Initial Active Directory Attributes
Now the BadAdmin performs the changes shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3 using Active Directory Users and Computers.
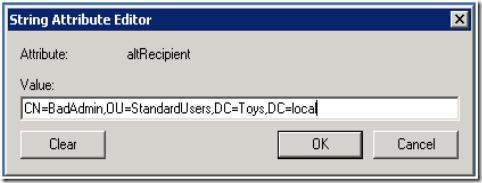
Figure 2: AltRecipeint
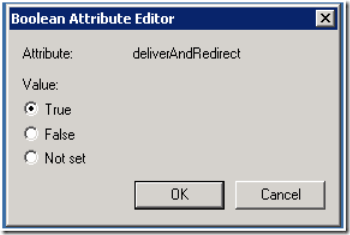
Figure 3: DeliverAndRedirect
I am sure you can guess the consequence of this modification.
These two changes will not be logged in the Exchange Administrator Audit Log. Therefore, it is important to add auditing of changes made to Active Directory objects to your plan.
18
Jan
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on The “Link” Used by a Linked Mailbox
In a resource forest topology the Exchange servers and the Exchange recipients are located in a separate Active Directory (AD) forest called resource forest – forest B in Figure 1. The user accounts are located in the so-called account forest – forest A.
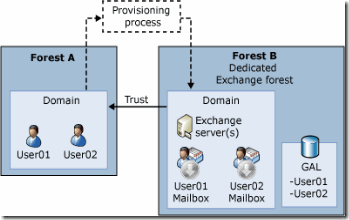
Figure 1: Resource Forest (Source Microsoft TechNet)
The resource forest trusts the account forest. The user account in the resource forest is disabled and only the mailbox of the disabled account is used. The AD account in the account forest is enabled. This is the account that you use to logon to your computer.
Let’s use PowerShell to investigate how the mailbox in a resource forest is linked to the user in the account forest.
In my test lab I have a mailbox in the resource forest with the alias “PennyM”. The account forest is called “Corp”.
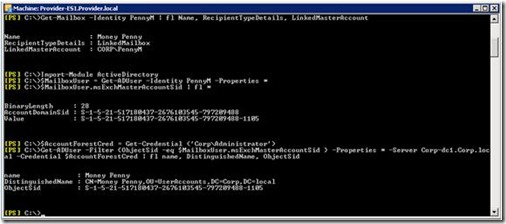
Figure 2: Linked Mailbox Attributes
The Exchange Management Shell command in Figure 2 shows that this mailbox is linked to the account Corp\PennyM in the account forest. The following two Get-ADUser commands from the ActiveDirectory PowerShell module are used to show the link between the two objects. The disabled account in the resource forest has an attribute called msExchMasterAccountSid that stores the value of the objectSid attribute of the corresponding user in the account forest.
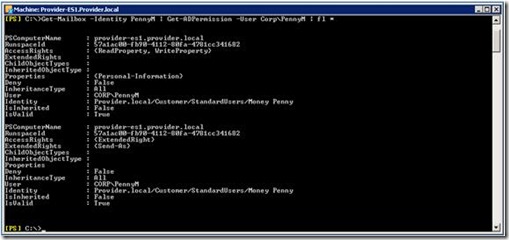
Figure 3: AD Permissions
Figure 3 shows that the user in the account forest was granted send-as rights and read property / write property rights on the personal information property set. These rights are granted when you create the linked mailbox.
Write access to the personal information property set enables the user in the account forest to modify for example the publicDelegates AD attribute of the disabled account in the resource forest. This AD attribute is modified when you execute the Delegate Access wizard in Outlook. It controls who can send mails on behalf of you.
Please refer to the TechNet article "Property Sets in Exchange 2007" for a description of the included attributes in the personal information property set.
18
Jan
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Auto-mapping of Shared Mailboxes in a Resource Forest Topology
Starting with Exchange Server 2010 Service Pack 1, Outlook automatically opens mailboxes where an Exchange administrator has granted you full access permission. This is for example explained in an article written by Steve Goodman. This feature use the Active Directory attributes msExchDelegateListLink and msExchDelegateListBL. AutoDiscover populates the AlternativeMailbox attribute to inform Outlook about these shared mailboxes. The same attribute is used to inform Outlook about your personal archive mailbox.
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0024_thumb.jpg)
Figure 1: AutoDiscover AlternativeMailbox
Starting with Service Pack 2 you can use the parameter -AutoMapping $false with the Add-MailboxPermission command to disable the auto-mapping feature.
However, there is still an issue if you use a resource forest topology.
In a resource forest topology the shared mailbox is located in the resource forest and the account that gets permission on this shared mailbox is located in the account forest. In my test lab the account forest is called “Corp” and the resource forest is called “Provider”.
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0044_thumb.jpg)
Figure 2: Full Access Granted to the Account Forest User
Figure 2 shows that the attributes msExchDelegateListLink and msExchDelegateListBL are not set after you execute the Add-MailboxPermission command.
Additionally you have to provide full access permission to the disabled account of the linked mailbox in the resource forest.
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0064_thumb.jpg)
Figure 3: Full Access Granted to the Disabled Resource Forest User Object
Please be aware that only granting full access permission to the disabled resource forest user object of the linked mailbox does not work. Outlook would automatically map the shared mailbox, but you would not be able to open the mailbox. You will receive the error message “Cannot expand the folder” if you try to access the shared mailbox.
15
Jan
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Microsoft iSCSI Software Target and VMware ESXi 5
Currently I do some self-study for updating my VMware professional certification to VCP5. In my lab at home I use the Microsoft iSCSI software target as shared storage solution. I know this configuration is not on the VMware Compatibility Guide, but it does not matter to me, as this setup is not used for production.
In the past I used the Microsoft iSCSI software target version 3.3 for Windows Server 2008 failover clustering experiments. This time I connected my ESXi 5 host to a virtual machine running on Hyper-V with the Microsoft iSCSI software target installed.
Very soon I run into issues with this setup. The vSphere Client showed the events in Figure 1.
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0025_thumb.jpg)
Figure 1: ESXi Events
The event viewer of my Windows Server 2008 R2 virtual machine showed a lot of error message like this one.
![clip_image004[5] clip_image004[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0045_thumb.jpg)
Figure 2: WinTarget Error Message
I found a note in the VMware Community that the iSCSI software target in Windows Server 8 does not have this issue. This was a perfect reason to start playing with Windows Server 8. The iSCSI target server can be installed using the Server Manager of Windows Server 8.
![clip_image006[5] clip_image006[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0065_thumb.jpg)
Figure 3: Server Roles
If you already know a previous version of the Microsoft iSCSI software target, then it will be easy for you to configure iSCSI virtual disks and iSCSI targets in Windows Server 8.
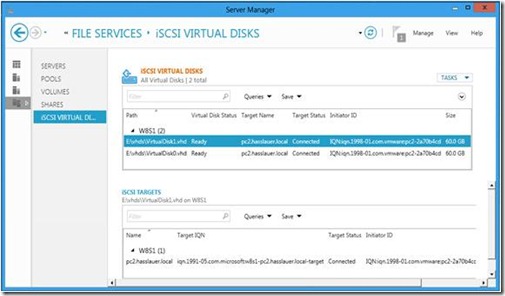
Figure 4: iSCSI Management
So far my ESXi 5 host is happy with the new setup.
15
Jan
2012
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on Resolving DNS Names with PowerShell 3.0
I am currently working for a large Lotus Notes to Exchange Server 2010 migration project. The Exchange organization will have mailboxes using about 40 different primary SMTP email domains.
Last week I had to check if the AutoDiscover DNS entries have already been configured. I did not want to start NSLOOKUP and type 40 different names. This would be too time consuming and very likely I would make a few typing errors. I had a file with the AutoDiscover hostnames and I thought how I can automate the task. I could use a command prompt window and execute the following pipeline:
Type filename | nslookup
However, this was not what I was looking for, because very likely I have to create a nice table showing the DNS name and the corresponding IP address.
I searched how I can resolve DNS entries using PowerShell. Initially I was disappointed about my search result.
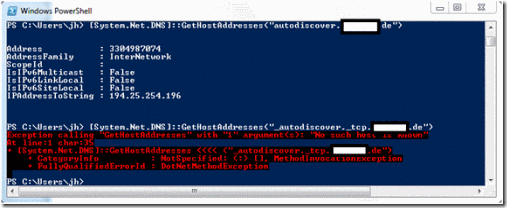
Figure 1: PowerShell Version 2
I could use the System.Net.Dns.GetHostAddresses method, but I found no method to resolve SRV records.
It looks like this issue will be fixed with PowerShell 3.0. On my Windows Server 8 system I found the new cmdlet Resolve-DnsName.
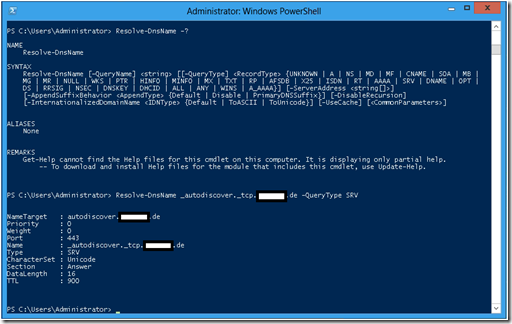
Figure 2: PowerShell Version 3
16
Oct
2011
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on The Experts Conference Europe 2011
Today I arrived in Frankfurt. In the afternoon I had a nice walk in the sun next to the Main River. From Monday to Wednesday I will attend The Experts Conference 2011 Europe. I will deliver two sessions for the Exchange track – “Built-in Exchange Server Functions to Control and Monitor Important Mailboxes” and “Preventing Information Leakage with Exchange Server 2010 Information Rights Management”. I am looking forward to go to interesting sessions and meet some old friends.
13
Mar
2011
Posted by Juergen. Comments Off on IT-Administrator Exchange Workshop
I will deliver a one day workshop for the IT–Administrator magazine about the following topics:
- High Availability in Exchange Server 2010
- Publishing Exchange Server with Forefront TMG
- Troubleshooting Exchange Server
Initially two events have been planned (April 14 in Hamburg and May 24 in Munich). However, they were sold out within a few days. Therefore, I will deliver two additional events – July 6 in Munich and August 16 in Hamburg. You can register for the event on the IT-Administrator magazine website.









![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0024_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0044_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0064_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0025_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image004[5] clip_image004[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0045_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image006[5] clip_image006[5]](http://hasslauer.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/clip_image0065_thumb.jpg)


